Impact of Blockchain on Insurance Industry
Do you know that nearly 80% of insurance executives have either already adopted or planning to pilot blockchain technology across their business units?
Well, the level of trust, transparency, and immutability that blockchain (distributed ledger technology) provides is impeccable. Blockchain offers an independently verifiable dataset so that insurers, as well as customers, need not suffer from decisions based on inappropriate/incomplete information.
In the instances of travel insurance, blockchain-based systems use external data sources to validate whether a flight was missed or cancelled.
Accordingly, insurers can decide on processing refund claims.
Well, blockchain can handle even more complex situations of road accidents by accurately determining the vehicle or human fault. Source
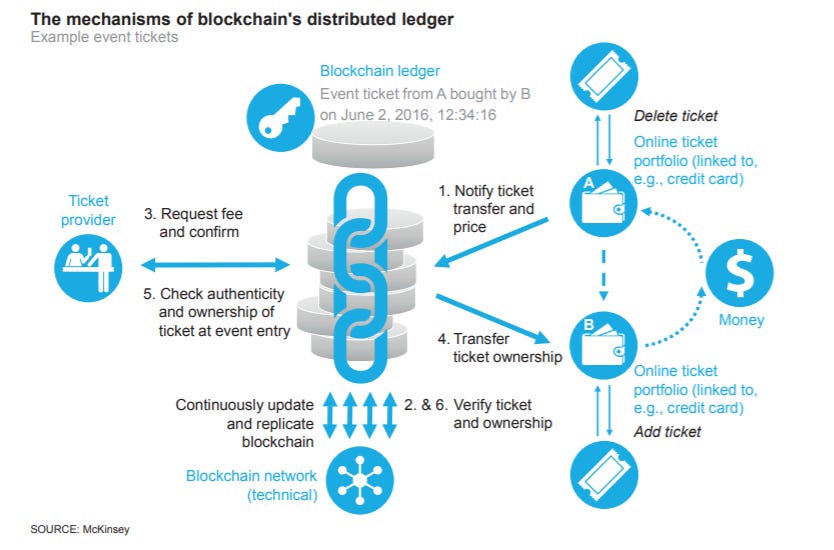
Blockchain is a distributed ledger that is broadly discussed as a technology with huge innovation potential in all areas of financial services. To date, it is largely in the banking arena where blockchain use cases have been identified. However, the blockchain technology also offers potential use cases for insurers that include innovating insurance products and services for growth, increasing effectiveness in fraud detection and pricing, and reducing administrative cost. In these application areas insurers could address some of the main challenges they are facing today – such as limited growth in mature markets and cost reduction pressures.
While implementation spans different layers – from infrastructure to generic platforms to specific applications – a blockchain solution, without requiring central coordination, generally builds on a set of four characteristics:
Decentralized validation- new data is packed into blocks that can only be added to the blockchain after consensus is reached on the validity of the action. This allows participants to place trust in their transactions even in the absence of a central authority, thus enabling disintermediation.
Redundancy- The blockchain is continuously replicated on all or at least a group of nodes in the network. As a result, no single point of failure exists.
Immutable storage- Each stored block is linked to its previous block in the chain, making it almost impossible for hackers to subsequently change blocks, as they would have to manipulate any succeeding block plus the majority of their replications.
Encryption- Digital signatures based on pairs of cryptographic private and public keys put network participants in a position to authenticate which participant initiated a transaction, owns an asset, signed a (smart) contract, or registered data in the blockchain. Source
In the banking industry, several blockchain use cases are currently being implemented, ranging from customer-facing payment technology to trading and exchange services.
While the insurance industry (in terms of technology adoption) lags behind banking, it is nevertheless uniquely positioned to benefit from blockchain technology. Blockchain can address the competitive challenges many incumbents face, including poor customer engagement, limited growth in mature markets, and the trends of digitization.
Let’s have a look at 3 practical blockchain use cases in the insurance industry:
Fraud and abuse prevention
Fraud costs the insurance industry monstrous amounts of money, mostly because it’s impossible to detect fraudulent activities with regular methods based on the use of publicly available data and private data sources. As a result, the accumulated data is usually fragmented due to legal constraints accompanying personally identifiable information.
Unfortunately, these gaps in visibility are being compromised by fraudsters. For example, multiple claims can be filed for a single case of care.
When data is stored on a blockchain-based ledger, it’s secured with cryptographic signatures and granular permission settings. It means that all the parties can share data and verify its authenticity without revealing sensitive information. A shared decentralized ledger facilitates historic data consolidation and helps companies spot suspicious patterns, such as:
Multiple processing of the same claim
An insurance policy’s ownership manipulation
Insurance sold by unlicensed brokers
To attain even higher security, insurance companies can provide customers with encrypted digital ID cards that can’t be faked. Source
Boosted transparency and trust
Insurance companies are called walled gardens for a reason. Customers have little chance to see how their data is managed. For example, they will never know that their data is shared with third parties. It’s no wonder that customers grow distrustful of insurance companies, particularly when facing long claim processing times or receiving claim denials—while the cost of premiums is ever-increasing.
However, when multiple insurance companies choose to contribute data to the same decentralized and shared ledger, it can lead to three big advantages:
Insurance companies can build more complete customer profiles and eliminate duplicate records. As the data in the blockchain ledger is immutable, the insurance companies won’t doubt its authenticity.
Customers will get visibility into what data their insurers have on them, and how this data is processed. Plus, when blockchain is combined with machine learning and AI, claim processing can be automated, thus accelerating pay-outs.
Blockchain helps automatically verify third-party claims or payments made through personal devices. Further on, the insurance company will be able to see all those transactions reflected on the blockchain.
Streamlined claim management
Selling and managing insurance policies is a labor-intensive process. In the context of high competition, insurance companies that stick to slow and paperwork-heavy traditional approaches lose to more digitally savvy competitors. The latter are able to offer lower premiums by automating claim management. Some of the processes can be automated by means of smart contracts which are getting popular for property and casualty insurance. When used in combination with connected devices, a smart contract can trigger automatic claim processing when, for example, anti-theft sensors go off under certain pre-programmed conditions.
The best way to reach this balance is to create a blockchain-based ecosystem with a considerable number of high-profile participants.
Once new records are added to the blockchain, the distributed ledger technology helps update and validate the data against other records in the network, which significantly reduces operating costs, at the same time providing high security for transactions.
The distributed ledger technology also deals with one more factor that slows down claim management—the need for bank transfers.
As a rule, customers don’t see pay-outs in their accounts for weeks. However, when banks and insurers have a single system they trust, the pay-outs can be processed without considerable delays.
The future of blockchain in the insurance industry
Blockchain is a decisive factor in transforming the insurance industry and helping it break free from outdated traditions. The need for innovation in insurance is critical—customers are craving transparency, speed and cost flexibility. Blockchain is designed to deliver on these desires and meet all the participants’ particular expectations.
When there’s little to no chance of fraud, people will trust their insurance agents more. When complex policy claims are processed 10x faster, there’s no room for friction. At the same time, when claim processing is automated, insurers have more possibilities to be flexible with pricing.
What’s more, the covered use cases are just the beginning. With more blockchain-based applications going live and more companies entering into collaborations, the insurance industry can grow its tech ecosystem to create better products for case management, audit, and risk modeling.
For further queries around blockchain/insurance use cases, please feel free to drop us a word at contact@artivatic.ai